CHAPTER III: PRESUPPOSED And CONDITIONS FOR The REALIZATION OF A VIRTUAL WAREHOUSE
To the day today particular attention is concentrated to the centers of analysis better known
like centers than cost. Until some time it makes in the industrial accountings, the costs directly were attributed to the
products without to filter them to the imputation centers in which they had had origin. I use of the centers, by now of
great spread and use is particularly useful for the following reasons:
- Corrected imputation of the costs, especially for those indirect ones, to the single products; with the centers it
is that is avoided to charge of the costs to products for which in truth they have not been supported;
- Greater control
and responsibility of the various business areas;
- Availabilities of give to you in the decisional processes on
the single operating units.
In practical the construction of the cost of a product it happens based on the appraisal
of two different tipologie of cost: the direct costs and the indirect costs.
The direct costs are easy attributable to
a product or one production store clerk, like as an example: the costs supported for the purchase or the extraction of the
raw materials, for the working to the aim to obtain a finished product. The indirect costs are, for the greater part, derive
to you from representation and commercialization, administration costs. Through the procedure of the cost centers it will
be possible to define of the models by means of which the indirect costs come decomposed and you are shared on several the
products.
The decomposition of the cost happens through the method of the division proporziona them that it is based on
the center concept.
Poichè a indirect cost cannot be attributed to the product that has supported it, then is attributed
to its center of belongings.
The center constitutes a recognizable independent entity univoca and to the inside of the
corporate structure (a company is composed therefore in more centers).
Every single product receives a quota cost reported
to a center in proportion to the use that it has made of the center. The usury of the center can be based on a any criterion
of reference:
- it can be the number of worked hours;
- the number of produced amounts;
- the employed time machine;
- the meters you
squared of the premises;
The subdivision of the company in centers demands however that these have requirement of:
- to) Uniformità as far as the production unit;
- b) Homogeneity of the type of equipment of productive factors (blots
of it and men) and therefore of the relative costs you to the aim to avoid to charge to the products of the mediated costs that
not rispecchiano the truth. Also as far as the engagement man the parameters, in the work- in-process are diametrically
opposite for which subdivision of centers becomes necessary to have one; quite where it blots some to them they were of
various nature and therefore of cost the une from the others the creation of a center for ciascuna can be rendered necessary
of they.
- c) Significance for which it is worth the pain to engage administrative resources that are not suffragate from a
effective return in terms of control and cost.
- d) Responsibility: it is necessary that for everyone of these centers
there is who then answers some.
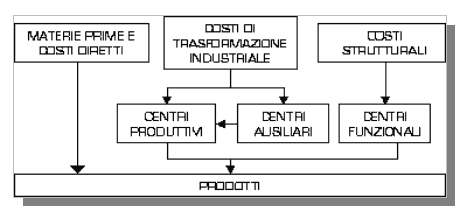
Figure n. 3.2 - Example of A.B.C.
To the aim to calculate the "true cost" attributable to a product, a diffused approach is the Activity Based Costing
.
This finds a precise the following motivation in consideration: between the product and the consumption of sure
resources not there is a direct tie. Therefore it is not the product that generates the costs directly and it cannot be
therefore the only object of calculation to which chargeing all the costs directly.
The product, in fact, for being obtained
and being sold demands that they come carried out of the activities and they are these last ones that consume resources and
generate the costs.
In this within the single activities are definable as that with of actions or elementary tasks that have
for objective that one to distribute a service or to indirectly produce output tangible (semifinished or a member of a product)
that it concurs, directly or, "to manifacture" the offer that the enterprise proposes its customers.
The degree of detail
with which these activities come defined can be much varied one and the choice cannot that to be consequent to the cognitive
requirementses you that it is placed to us in the specific case.
The analysis of the management for activity allows to
understand better than what organizational units happen to the inside of the functions and the correspondents and to pick
the ties between the functions and to manage the company as it arranges. Wanting to define it is made logical that the A.B.C.
second characterizes the introduction of a process of determination of the product cost, can be indicated following is made:
- to) the activities and the consequent one of the accounts slowly are defined, with the indication of the centers of cost
for activity (activity cost pool),
- b) the costs and objective to attributable they are attributed specifically to the
activities; draft therefore to determine the resources absorbed from the various activities through of the pointers of
employment of the resources (resource driver) as they can be the hours man, the hours machine, the percentages of uses;
- c) the activities are characterized determining of cost (cost driver) relative to all and quantification is proceeded
to one they,
- d) the cost of the single activities for unit of determining is estimated of cost (cost driver),
dividend the cost total of the activity for the total value attributed to the determining one of cost,
- and) if it is thought necessary, it can also be proceeded to charge to cascade, through prechosen cost driver, the costs
from the activities of support, than reputa possible not to charge itself directly to the product, to the activities of
fabrication and sale; this indirect imputation is much debatable one, therefore some students suggests not to allot these
costs to the products in how much relating to activity to which often lacks whichever tie causalità directed with the product;
they are the activities destined to make to work the corporate structure in its complex;
- f) totals of the single activities to the products are chargeed the costs, multiplying the cost for unit of cost driver
for the value that the cost driver assumes with reference to the product calculation object.

